[最も共有された! √] q table for tukey hsd 193303-How to read tukey hsd table
Tukey HSD Test Tukey HSD Test for PostANOVA PairWise Comparisons in a OneWay ANOVA After performing a oneway analysis of variance, enter the values outlined in red, then click the Calculate buttonHSD = q o MSE / n* = 3 o 975 / 10 = The q value of 3 is obtained by reference to the studentized range statistic table looking up the q value for an alpha of 05, df = < = 32, k = pQ Distribution Table How to Use the Q Distribution Table This table should be used only if the sample sizes in your Tukey's HSD analysis are equal There are two sections of

Locating Variance Post Hoc Tests Ppt Video Online Download
How to read tukey hsd table
How to read tukey hsd table- Q = (177 – 167) / 1 – 167 = 10/22 = 0455 Step 3 Find the Q critical value in the Q table (scroll to the bottom of the article for the table) For a sample size of 7 and an alpha level of 5%, the critical value is 0568 Step 4 Compare the Q statistic from Step 2 with the QExplore more like Tukey HSD Tukey Test Tukey Q Table Tukey Critical Value ©21 Daily Search Trends FeedbackDaily Search Trends Feedback



Multiple Pair Wise Comparisons Using Tukey S Hsd And The Compact Letter Display Statistics With R
Tukey's range test, also known as Tukey's test, Tukey method, Tukey's honest significance test, or Tukey's HSD (honestly significant difference) test, is a singlestep multiple comparison procedure and statistical testIt can be used to find means that are significantly different from each other Named after John Tukey, it compares all possible pairs of means, and is based on a 1 Answer1 Active Oldest Votes 3 from statsmodelsstatslibqsturng import psturng, qsturng provides cdf (or tail probabilities) and quantile function (inverse of cdf or of survival function, I don't remember) It was written by Roger Lew as a package for interpolating the distribution of the studentized range statistic and was incorporated in Tabel HSD/Tukey pada taraf nyata 5% (Studentised 005 ) Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website
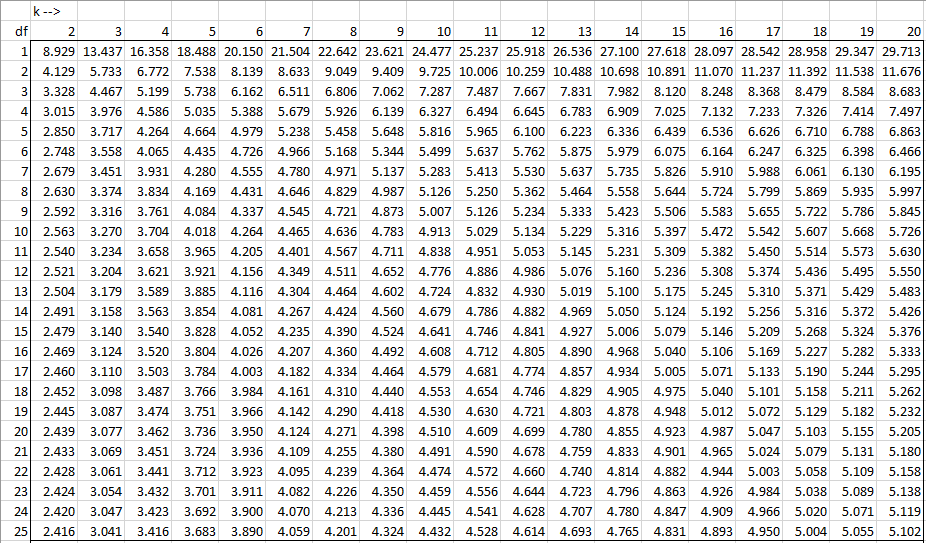
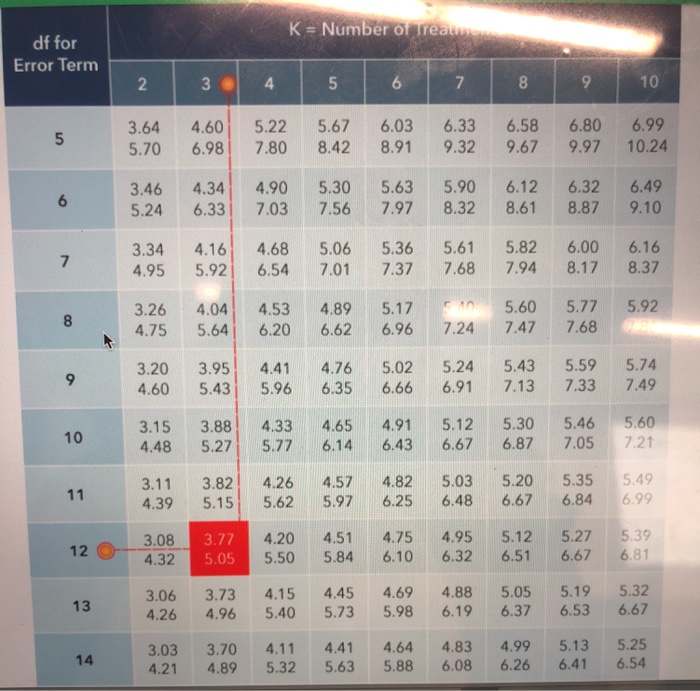
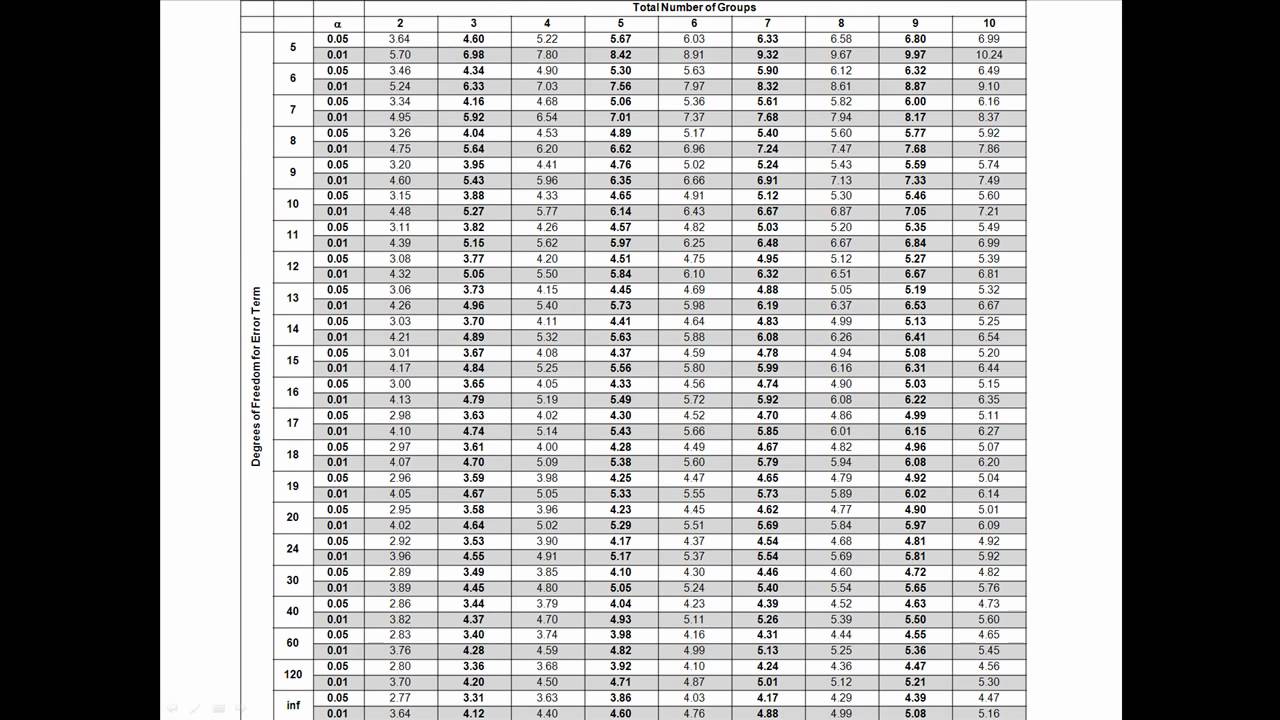
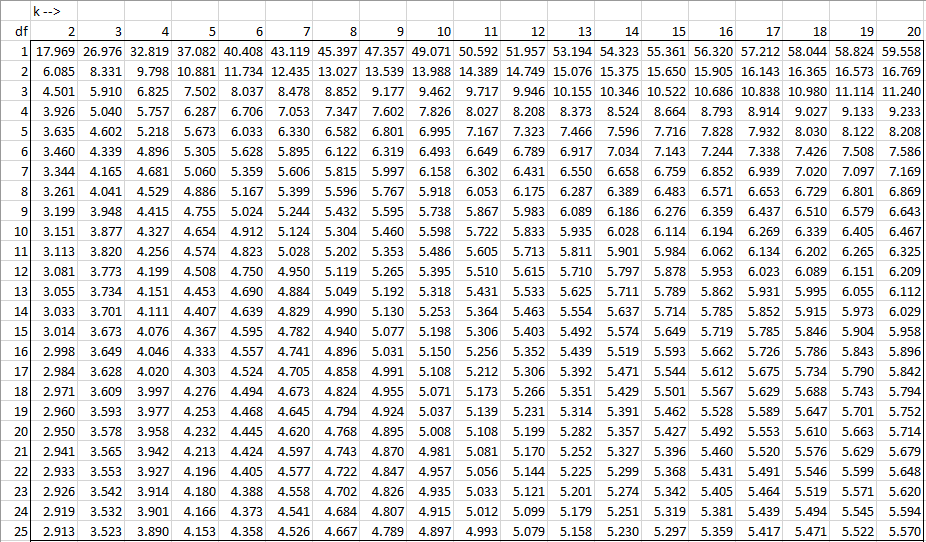
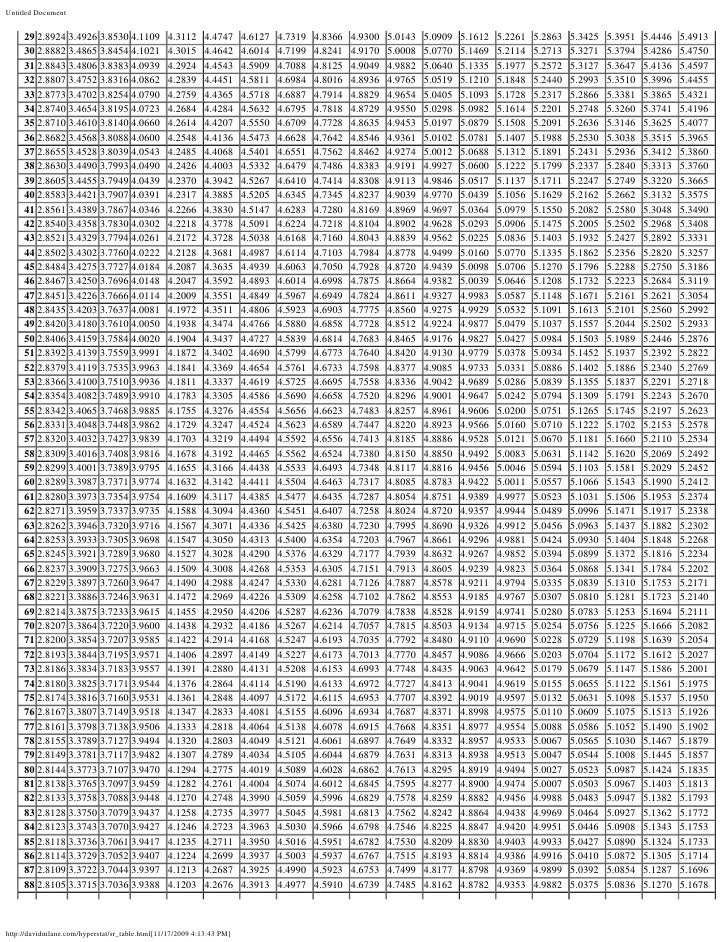
HSD =q Within ÅNote that "q" is a table value, and n is the number of values we are dealing with in each group (not total n) The Mean Square value is from the ANOVA you already computed To find "q" or the studentized range statistic, refer to your table on page A32 of your text On the table 'k' or the number of groups is found along theView Q Table for Tukey's HSDpdf from MATH 401 at Mbarara University of Science and TechnologyMbarara Q Table for Tukey's HSD TABLE B5The studentized range statistic (q)* *The criticalCritical values of the studentized range distribution (Q) are commonly used in Tukey's range test A continuous probability distribution that arises during the estimation of the range of a normally distributed population in circumstances where the population SD is unknown and the size of the sample is also less is called as the Studentized range distribution
TukeyHSDResults (mc_object, results_table, q_crit, reject = None, meandiffs = None, std_pairs = None, confint = None, df_total = None, reject2 = None, variance = None, pvalues = None) source ¶ Results from Tukey HSD test, with additional plot methods Can also compute and plot additional posthoc evaluations using this results class Notes9 Tukey's HSD test Sleep apnea is a disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep Children who suffer from untreated sleep apnea often have behavior problems, including hyperactivity, inattention, and aggression A common treatment for pediatric sleep apnea is the surgical removal of enlarged tonsils and adenoids that are as it is now it doesn't loop, I struggled to get the Tukey HSD into table, When I have it I want to find the significant values p adj, I get also confused about adding a column that would say what protein are these values for I imagine it as a column first column containing one name for as many rows as it needs for out put thanks a lot!
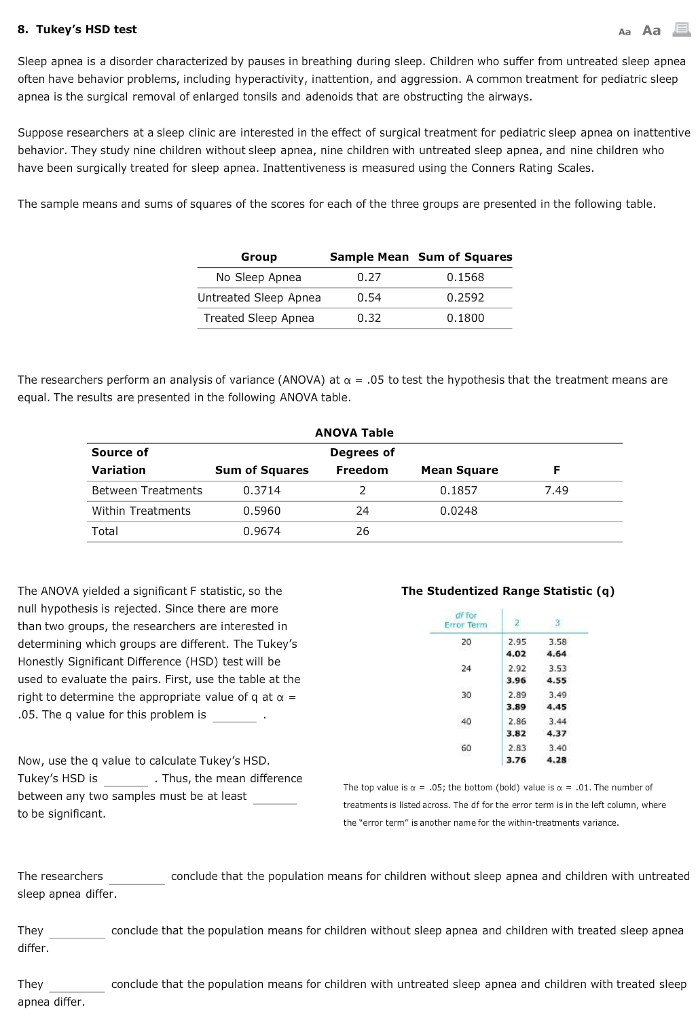



8 Tukey S Hsd Test Sleep Apnea Is A Disorde Chegg Com




Locating Variance Post Hoc Tests Ppt Video Online Download
Tables of the inverse Studentized Range distribution, such as this table at Duke University Next, we establish a Tukey test statistic from our sample columns to compare with the appropriate critical value of the studentized range distribution We take the TukeyKramer confidence limits as documented in the NIST Q statistic Tukey HSD pvalueFrom Q Jump to navigation , search Tukey's Honestly Significant Differences (also known as Tukey's Whole Significant Differences ) The test statistic is t = x ¯ 1 − x ¯ 2 ∑ j = 1 J ∑ i = 1 n j w i j ( x i j − x ¯ j ) 2 v ( 1 e 1 1 e 1 ) {\displaystyle t= {\frac { {\bar {x}}_ {1} {\bar {x}}_ {2}} {\sqrt { {\frac {\sum _ {j=1}^ {J}\sum _Używam Posthoc Tukeya HSD na przetwarzanie moich danych, który ma dziesięć poziomów czynnika Stół jest masywny i został nadzieją tylko przedstawienie wartości p dla czytelnika, parami w tabeli pozostawiając Tabela 45 wiersz ED dla dodatku Oto




Tukey S Hsd Table Of Q Statistics For Esn Model Download Table




Anova And Tukey S Hsd Test Results Download Table
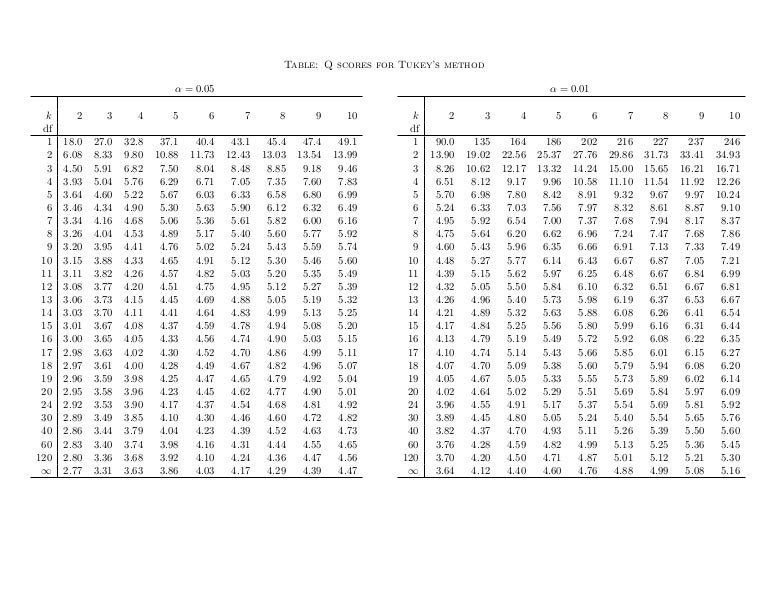
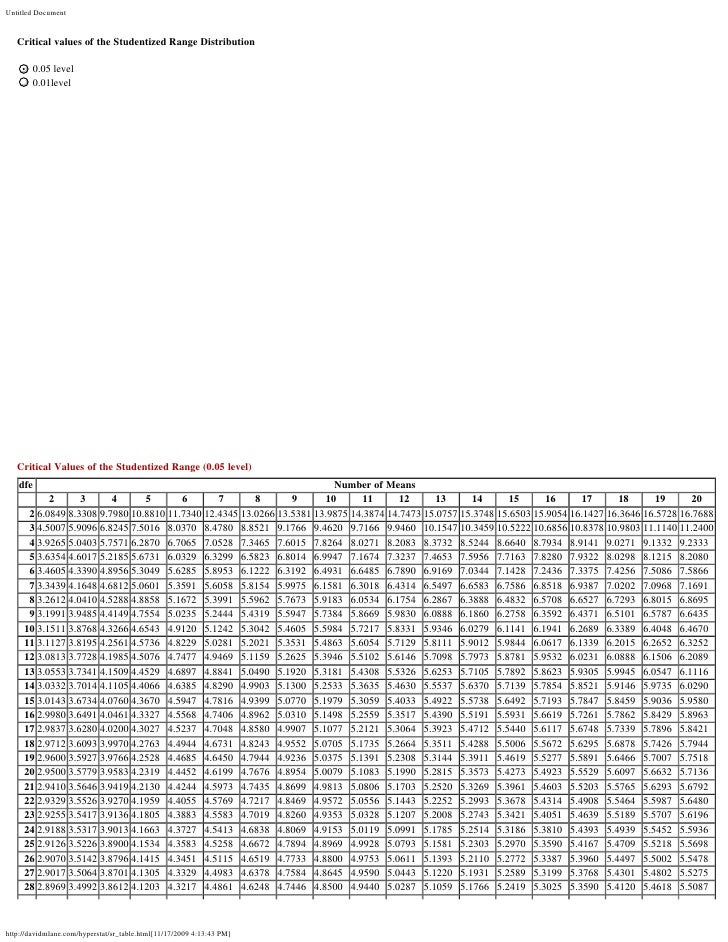
The Studentized range upper quantiles q(k,df;010) df 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1 29 184 150Well, the histograms and means tables we ran before our ANOVA point us in the right direction However, we'll try and back that up with a more formal test Tukey's HSD as shown in the multiple comparisons table Right, now comparing 4 means results in (4 1) x 4 x 05 = 6 distinct comparisons, each of which is listed twice in this table Tukey Table 1 Table Q scores for Tukey's method α = 005 k df 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 24 30 40 60 1 ∞ α = 001 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 180 608 450 393 364 346 334 326 3 315 311 308 306 303 301 300 298 297 296 295 292 2 286 2 280 277 270 3 591 504 460 434 416 404 395 3



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Sage Reference Encyclopedia Of Research Design
Summary, recommended MCP methods that use the Q‐distribution such as the Tukey HSD, REGWQ, and Games‐Howell tests As formulas for this distribution are not available in Excel, it was logical to make a simple user‐defined function and implement Studentized range quantiles (Q What would the critical value (Tukey's HSD) be for our job applicant scenario?Q Calculator (Studentized Range Distribution/Tukey HSD) The inputs below are straightforward Your q score goes in the first box The number of groups (or treatments, means, etc) in your study goes into the second box And you add the withingroups degrees of freedom to the final box




12 7 Tukey S Honestly Significant Difference Post Hoc Test Youtube




Tukey S Hsd Table Of Q Statistics For Esn Model Download Table
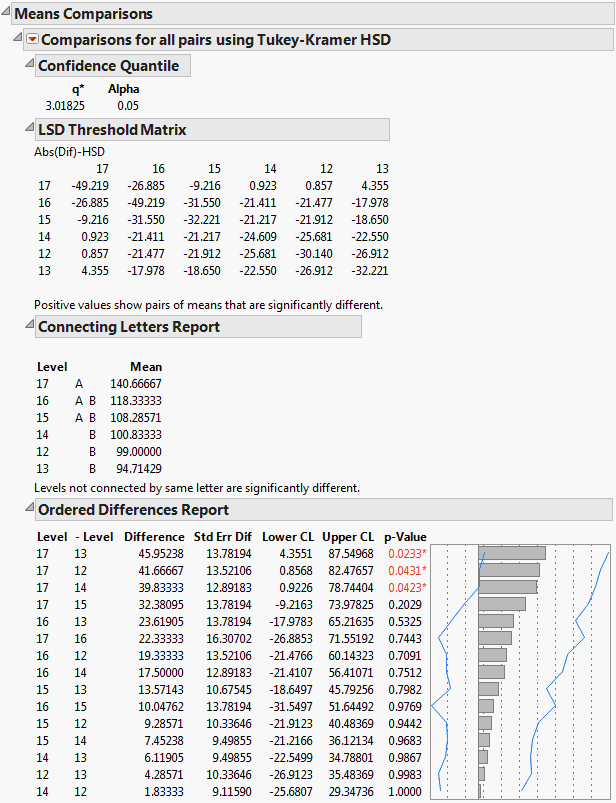
Sarah, You would need to interpolate between the table values for df = 1 and df = 240 Qcrit for df = 1 is 3685 and the Qcrit for df = 240 id 3659 A linear interpolation would give the value , which can be calculated using the Real Statistics formula =QCRIT(4,156,005,2)> oldpar par(mai=c(15,2,1,1)) #Makes room on the plot for the group names > plot(Tm2) Figure 218 Graphical display of pairwise comparisons from Tukey's HSD for the Guinea Pig data Any confidence intervals that do not contain 0 provide evidence of a difference in the groupsCritical Values of Studentized Range Distribution(q) for Familywise ALPHA = 05 Denominator Number of Groups (aka Treatments) DF 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 31 9798 101 3 5910 65 7502 8037 8478 52 9177 9462



Vslpcumq2mpdmm



Rpubs Com ronsc32 Post Hoc Analysis Tukey
Table Q scores for Tukey's method α = 005 α = 001 k 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 k 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 df df 1 180 270 328 371 404 431 454 474 491 1 900 135 164 How do you find q in Tukey's HSD?Tukey HSD (Honestly Significant Difference) The idea behind the Tukey HSD (Honestly Significant Difference) test is to focus on the largest value of the difference between two group means The relevant statistic is and n = the size of each of the group samples The statistic q has a distribution called the studentized range q (see Studentized



3




Q Table For Tukey Pdf Table B 5 The Q Statistic Tukey Hsd Test K Number Of Treatments Levels Withingroups Df Alp Ha Lev El 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Course Hero
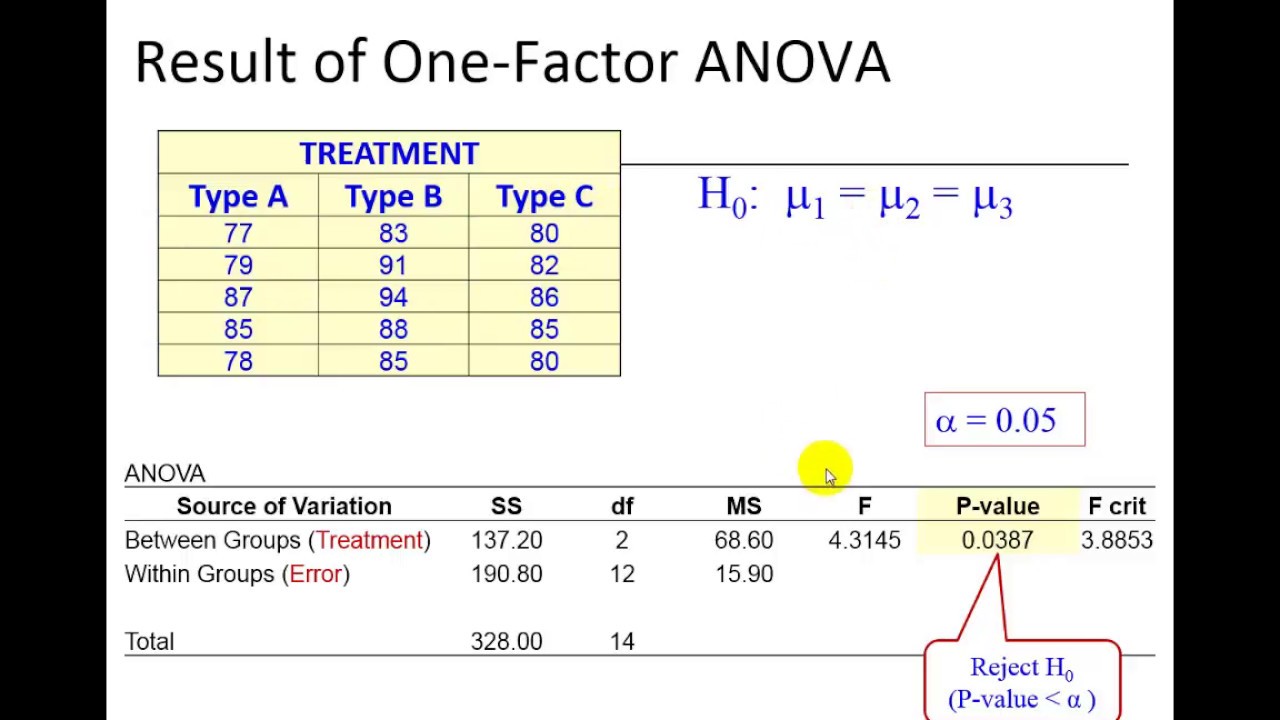
A Tukey test works better than a Bonferroni correction, but it only works with ANOVA (Bonferroni works with many tests) Tukey's test works very similarly to a twosided ttest, but with larger critical values At df=, for example The tcritical is _____ The Tukey critical is _____ for 3 groups and is _____ for 4 groupsThe Tukey HSD test calculates Test Statistic q for each pair of means This Test Statistic is compared to q Critical The critical q values are found on the Studentized Range q table using the Excel lookup function, INDEX(array, row number, column number)Lesson 16 Posthoc Tests Outline Tukey's HSD Posthoc test For the Tukey's posthoc test we will first find the differences between the means of all To find "q" or the studentized range statistic, refer to your table on page lesson 16pdf




Tukey Hsd Test What Is The Tukey Hsd Test




Tukey Hsd All Pairwise Comparisons Test Of Caratenoid Download Table
Tukey Q Calculator This tool will calculate critical values (Q 05 and Q 01) for the Studentized range distribution statistic (Q), normally used in the calculation of Tukey's HSD The calculator is easy to use Just input the number of groups in your study (k) in the first box, and degrees of freedom (normally the total number of subjects minusTukey's HSD Tukey's HSD is a multiple comparison technique that tests the null hypothesis that two means are equal It should be used when you reject ANOVA's omnibus null hypothesis AND the number of levels of the IV is greater than 2 H 0 μ 1 μ 2 = 0 or H 0 μ 1 = μ 2 H 1 μ 1 μ 2 ≠ 0 H 1 μ 1 ≠ μ 2 HSD=qk,df,α× For exaplanatory purpose, I tried to make up a function which provides full Tukey Table, see my comments inside I still think that the Rhelp is misleading in this case QTable




Tukey S Hsd Table Of Q Statistics For Esn Model Download Table




Turkey Hsd檢驗法 W法 碼上快樂
Solution Let's first find the qvalue We know that we have 3 groups (k = 3), and 30 participants The \(df_{W}\) is calculated as N – k, so that's 30 – 3 = 27 According to the Alpha = 005 table at https//wwwrealstatisticscom/statrangeqtable/, q = 3506The Tukey HSD test then uses these critical values of Q to determine how large the difference between the means of any two particular groups must be in order to be regarded as significant The other participants in this determination, MS wg and N p/s, are the same items you saw in the earlier formula for QThe following two "HSD" formulas are simply algebraic jugglings of the originalTukey Test and Linear Regression Say there are four groups, (a,b,c,d), for one feature in a dataset with many features I am trying to predict a numerical feature y I perform the Tukey test and find that the means of y for groups a regression categoricaldata tukeyhsdtest asked Dec 16 ' at 1703 Morgan Lu



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel



Tukey Method One Way Anova Youtube
Q table for Tukeypdf TABLE B5 The q Statistic (Tukey HSD School Pierce College Course Title STAT 101 Uploaded By pollolocorty5 Pages 3 This preview shows page 1 3 out of 3 pages View full document TABLE B5 The q Statistic (Tukey HSD Test) k = Number of Treatments (Levels) Within Groups df Alp ha Lev el 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 4 0 To find the Q value, you can refer to the Studentized Range Q Table which looks like this In our example, k = the number of groups, which is k = 3 The degrees of freedom is calculated as nk = 30 – 3 = 27 Since 27 is not shown in the table above, we can use aTukey Kramer HSD Test calculator Tukey Range test is the other name of tukeykramer and it is a single step process which compares multiple procedes and the statistical test, which is used in the conjunction with One Way ANOVA to find the means that are significantly different from each other




Analysis Of Variance Anova Quantitative Methods In Hpels



9 09 What Is The Tukey Hsd Critical Value For A Chegg Com
This video demonstrates how to calculate the Honestly Significant Differences for pairwise comparisons of means that have been shown through an analysis of vFirst thing you must remember while moving on to post hoc analysis is the null hypothesis of the analysis of variance must be rejected, so that we can claim there exists a difference in the group means Now, once we achieve that the tukey HSD can be performed simply by using TukeyHSD function in base R Download Q Table Tukey Images 1 Builds a table with quantiles of the sample relative range distribution Post Hoc Tests For One Way Anova from wwwstatisticslecturescom Savesave q table tukey kramer for later



Post Hoc Tests For One Way Anova Youtube




Q Table For Hsd Table 3 5 The Studentized Range Statistic Q The Critical Values For Q Corresponding To A 05 Lightface Type And A 01 Boldface Type Course Hero
To find " q " or the studentized range statistic, refer to your table on page A32 of your text On the table 'k' or the number of groups is found along the top, and degrees of freedom within is down the sideANOVA Tukey's HSD Test Application Oneway ANOVA – pairwise comparison of means Requirements Model must be balanced, which means that the sample size in each population should be the same The samples taken in each population are called replicates Each population is called a treatment (Note There are methods of approximating this model if the design is notTukey HSD Test by hand Tukey HSD Test by hand Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device



Methods Sagepub Com Base Download Referenceentry The Sage Encyclopedia Of Communication Research Methods I Xml




Category Tests Of Statistical Significance Q
How to perform tukey HSD in base R?Liczba wierszy 24 Q Table for Tukey's HSD TABLE B5 The studentized range statistic (q)* *The critical values for q corresponding to alpha= 05 (top) and alpha=01 (bottom) dffor Error Term k=Number of Treatments 2



Www Ars Usda Gov Arsuserfiles Rapidcalculationofq Pdf




Locating Variance Post Hoc Tests Ppt Video Online Download




Tukey Test In Factorial Experiment Cross Validated
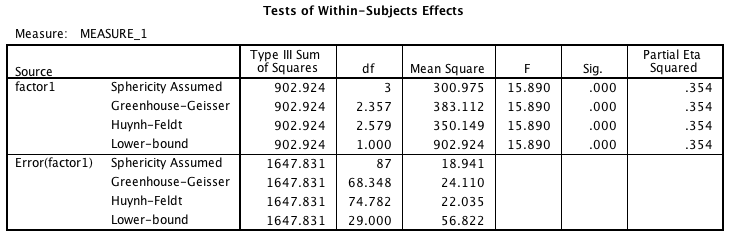



Tukey S Hsd Test Motor Behaviour




Multiple Pair Wise Comparisons Using Tukey S Hsd And The Compact Letter Display Statistics With R
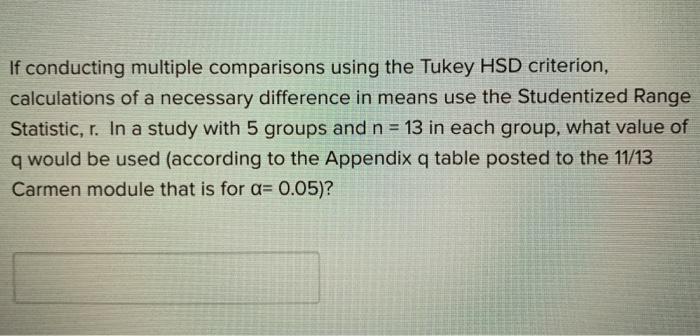



If Conducting Multiple Comparisons Using The Tukey Chegg Com



Newman Keuls Test And Tukey Test Sage Research Methods




How To Report Tukey Hsd Results




Oneway Anova Introduction To Analysis Of Variance Anova
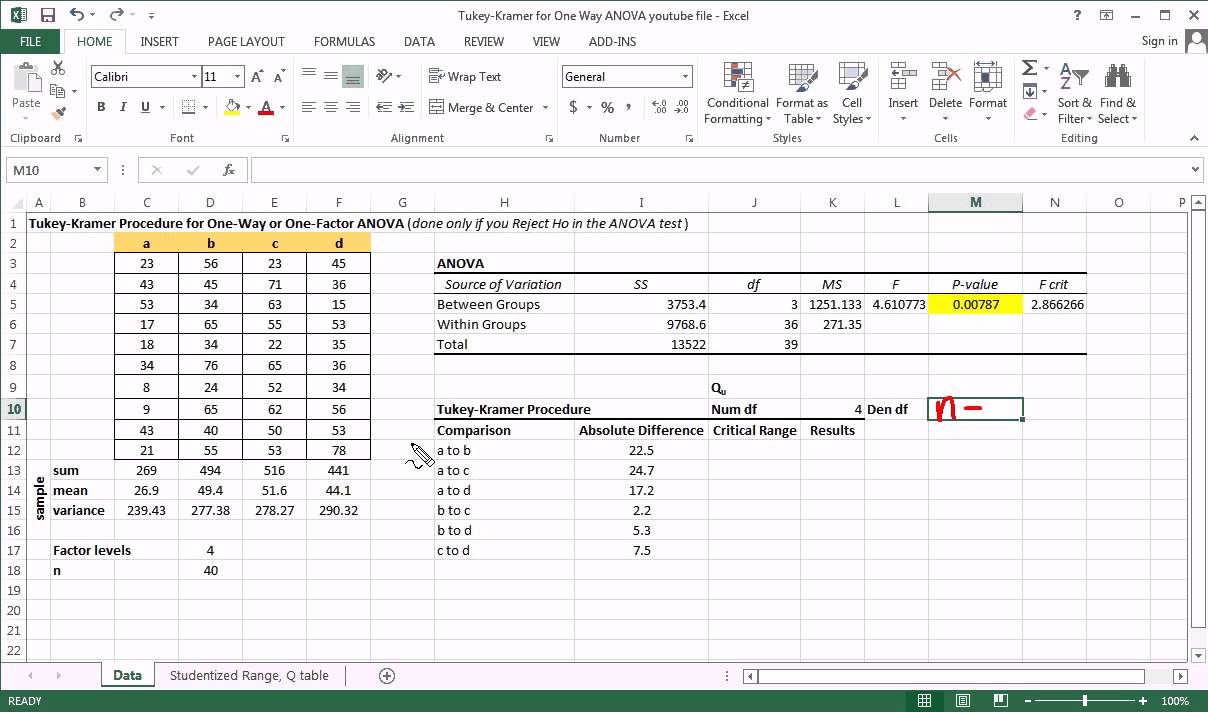



Tukey Kramer Multiple Comparison Procedure And Anova With Excel Youtube
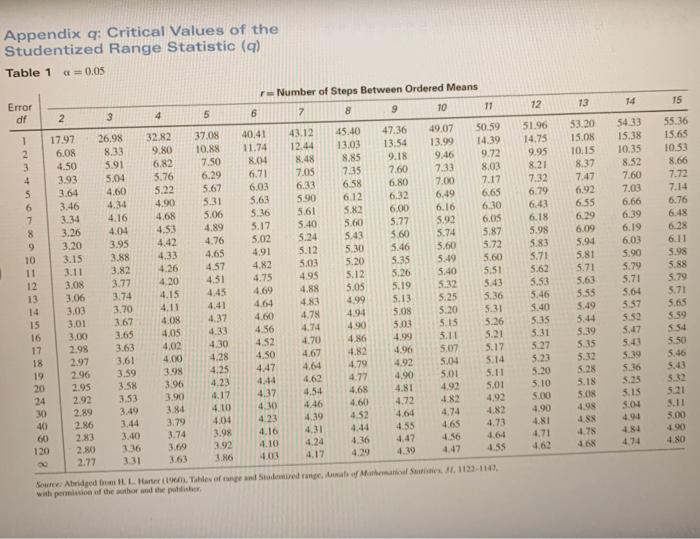



If Conducting Multiple Comparisons Using The Tukey Chegg Com




How To Perform A Tukey Kramer Post Hoc Test In Excel Statology




Tukey S Test Professor Mckee S Things And Stuff




Lesson 14



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Analysis Of Variance Anova Quantitative Methods In Hpels



Uma Ac Ir Find Php D 1 12 31 Fa



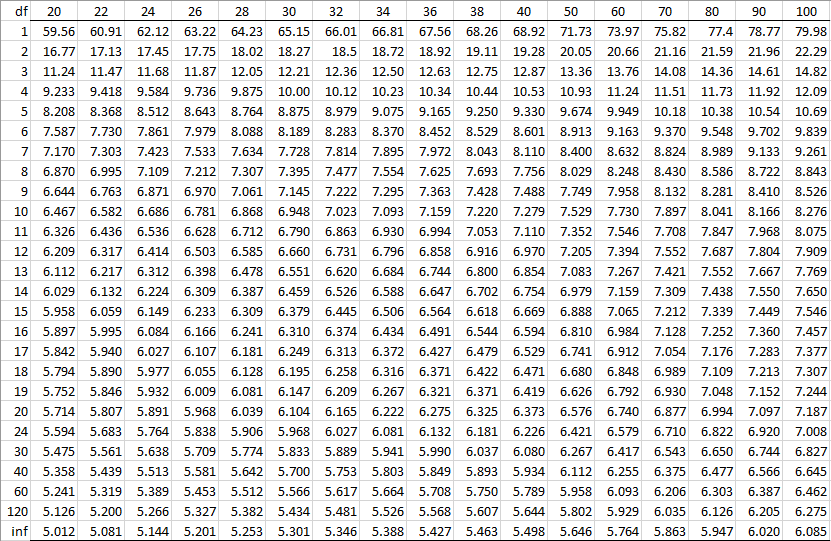
Studentized Range Distribution



Tukey Hsd Test By Hand Youtube




How To Obtain The Results Of A Tukey Hsd Post Hoc Test In A Table Showing Grouped Pairs Cross Validated



Example Of The All Pairs Tukey Hsd Test




Tukey Hsd Plot Simultaneous How Does It Work Cross Validated




Pdf Newman Keuls Test And Tukey Test




Anova And Tukey S Hsd Post Hoc Test Results For Affective Attribute Download Table
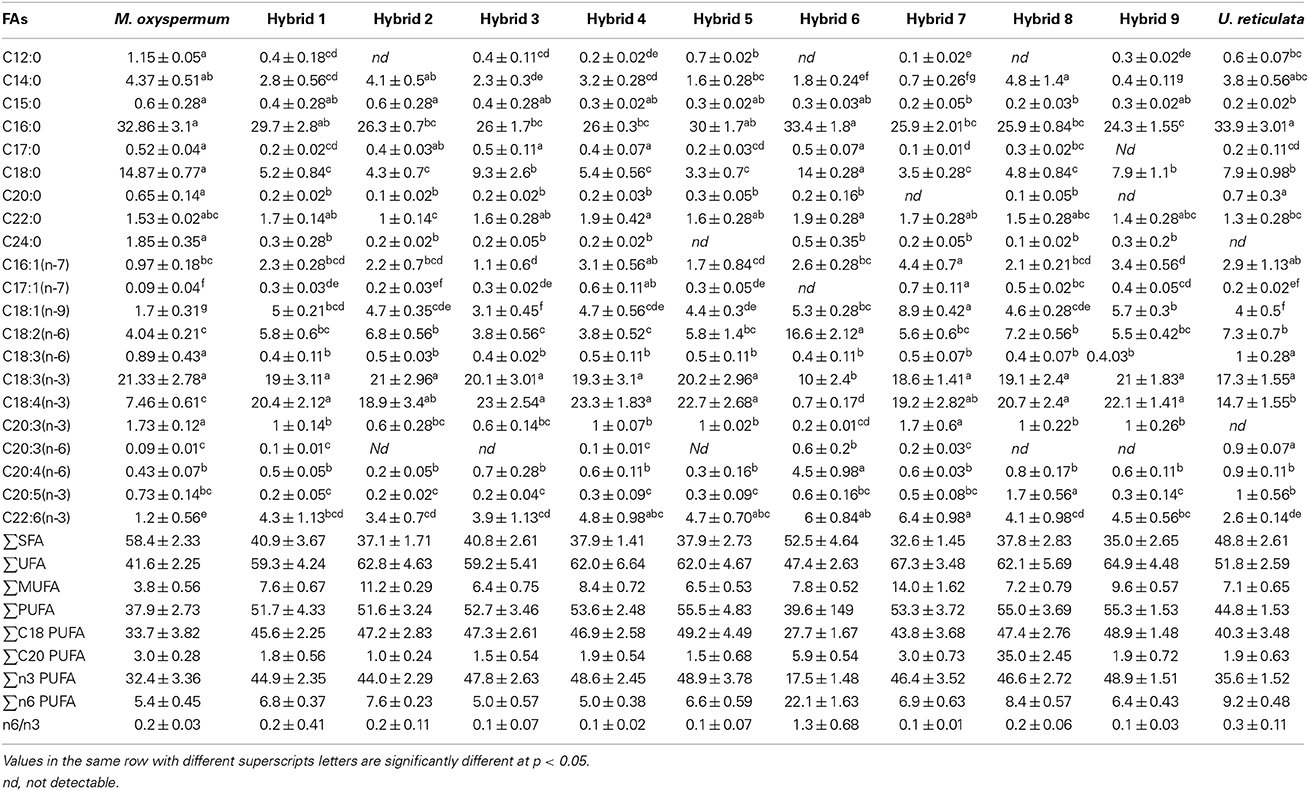



Frontiers Development And Characterization Of Somatic Hybrids Of Ulva Reticulata Forsskal Monostroma Oxyspermum Kutz Doty Plant Science



Solved Run A Tukey Test On The Example Given In Table Page 332 Chegg Com
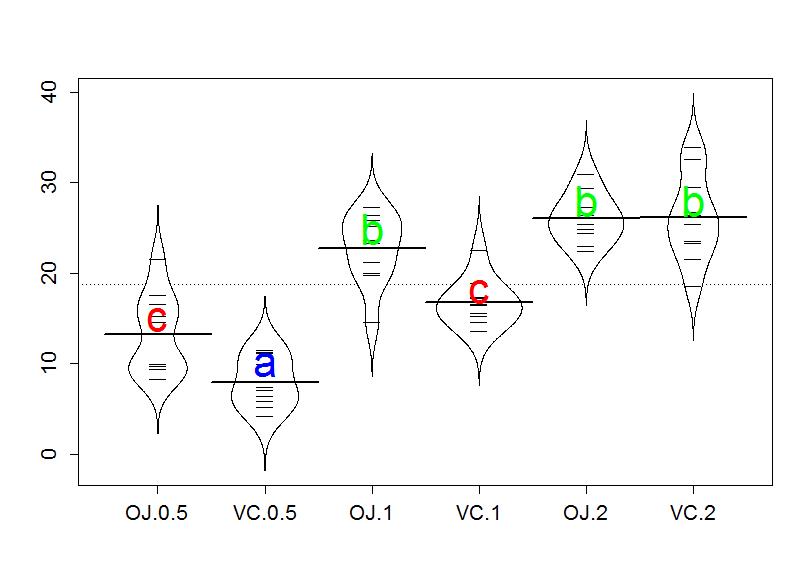



Multiple Pair Wise Comparisons Using Tukey S Hsd And The Compact Letter Display Statistics With R




Category Tests Of Statistical Significance Q




Newman Keuls Test And Tukey Test Sage Research Methods




Tukey Hsd Test Result Multiple Comparisons K 3 Download Table




Turkey Hsd檢驗法 W法 碼上快樂
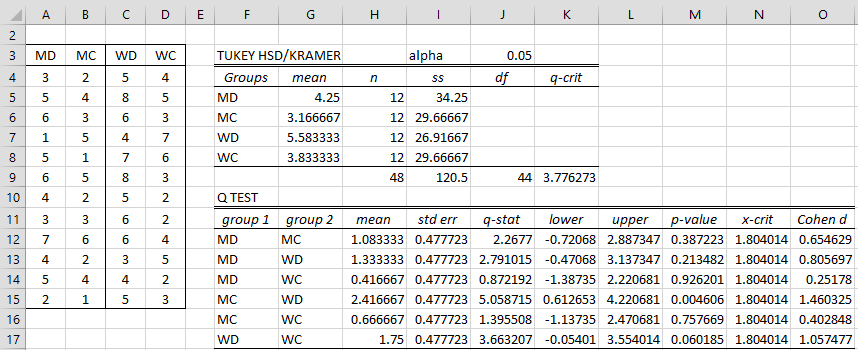



Tukey Hsd Real Statistics Using Excel



Multiple Comparisons




2 3 Mean Comparisons



1




T U K E Y T A B L E Zonealarm Results
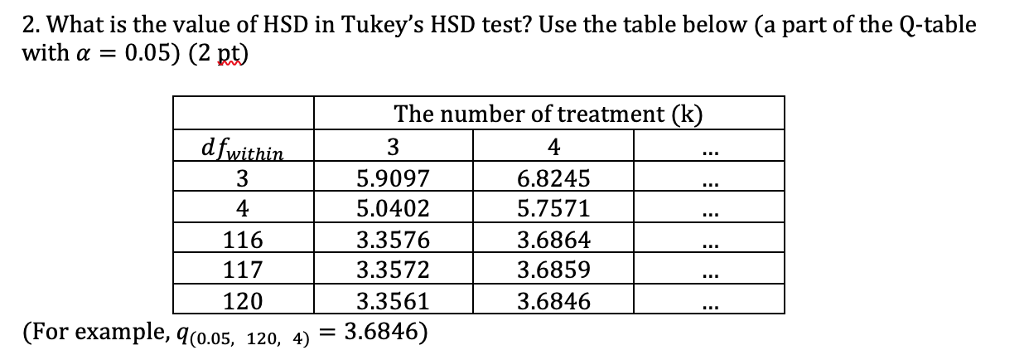



2 What Is The Value Of Hsd In Tukey S Hsd Test Use Chegg Com




How To Perform A Tukey Kramer Post Hoc Test In Excel Statology




How To Perform A Tukey Kramer Post Hoc Test In Excel Statology




Post Hoc Tukey Hsd Test For Hypothesis Where The One Factor Analysis Download Scientific Diagram




Tukey S Honestly Significant Difference Ppt Download



T U K E Y Q T A B L E Zonealarm Results
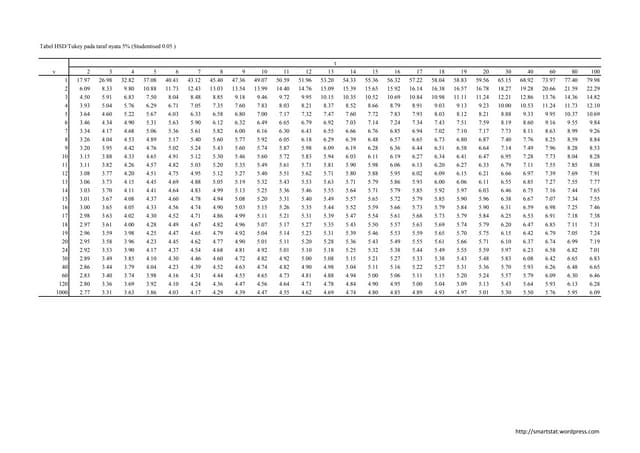



Tukey Q Table



One Way Anova Independent Samples Ii
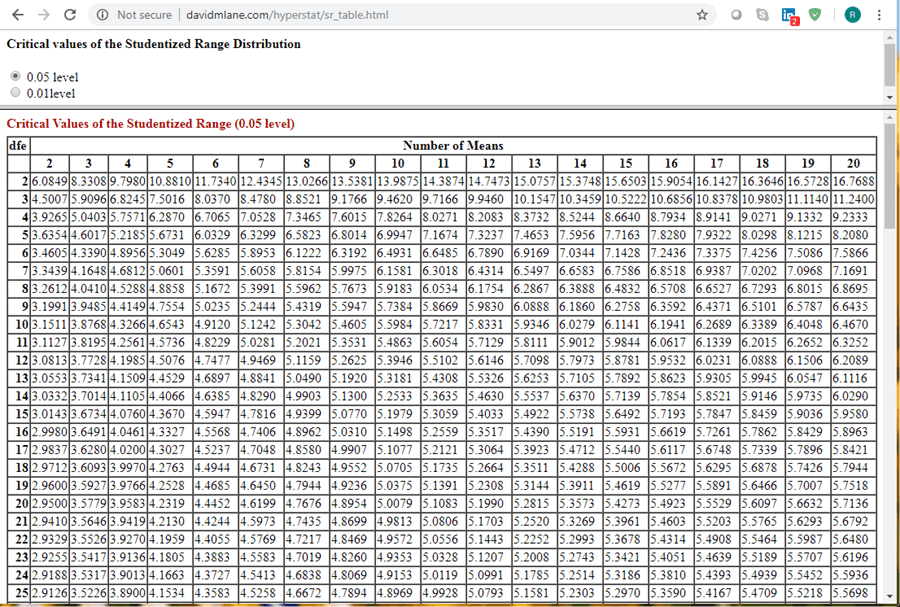



T U K E Y Q T A B L E Zonealarm Results




12 7 Tukey S Honestly Significant Difference Post Hoc Test Youtube




Tukey Q Table
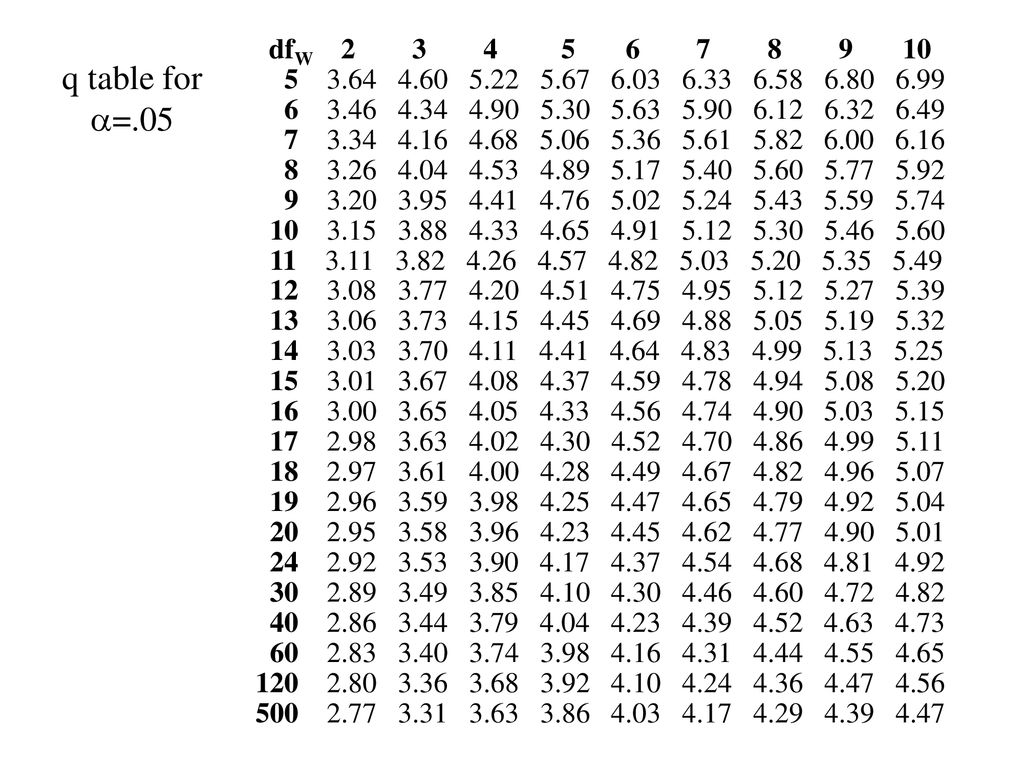



Tukey S Honestly Significant Difference Ppt Download




Descriptive Statistics To Describe Your Sample You Need




Post Hoc Tests Multiple Comparisons Tukey Hsd On Organizational Download Table
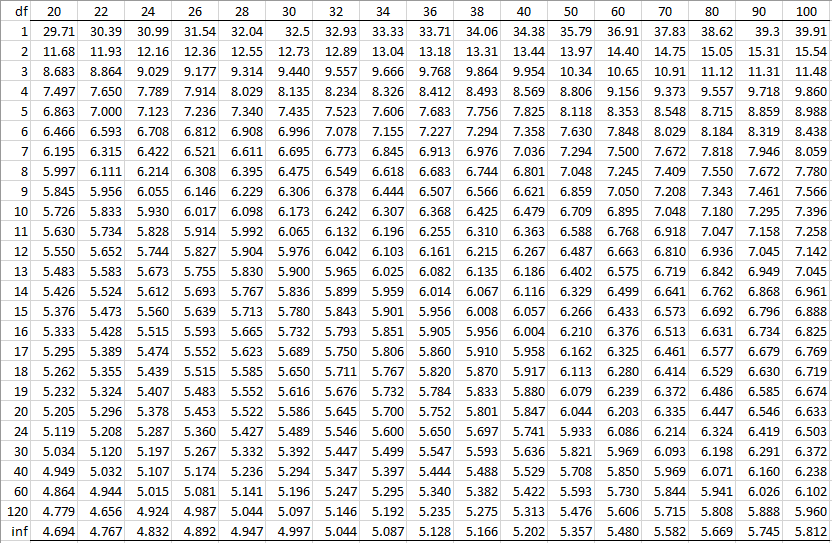



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel



1



Studentized Range Distribution



Studentized Range Q Table Real Statistics Using Excel




Tukeyhsd Twitter Search




Analysis Of Variance Anova Quantitative Methods In Hpels 440 Ppt Download




Post Hoc Tests What Is A Post Hoc




Tukey S Hsd Table Of Q Statistics For Esn Model Download Table




How To Perform A Tukey Kramer Post Hoc Test In Excel Statology
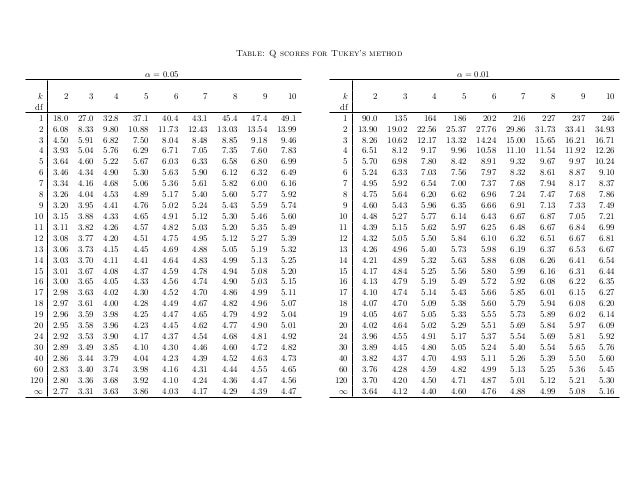



Vslpcumq2mpdmm
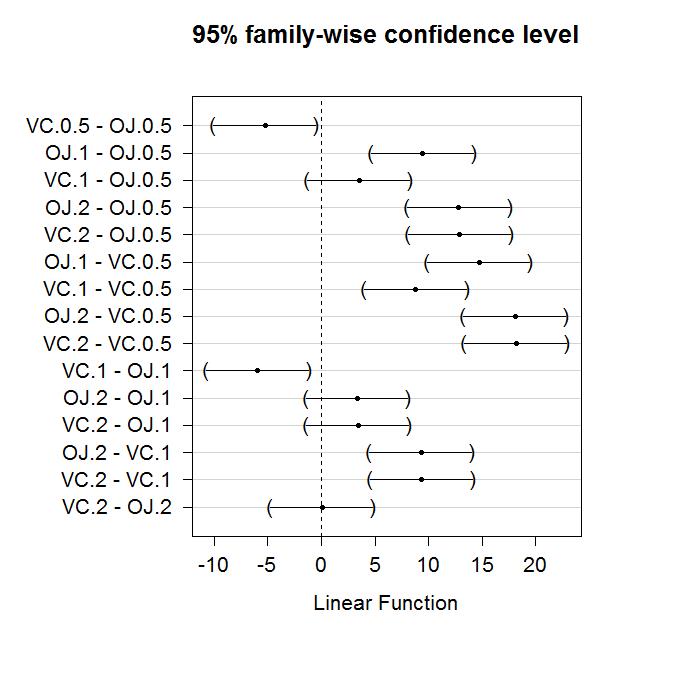



Multiple Pair Wise Comparisons Using Tukey S Hsd And The Compact Letter Display Statistics With R



Post Hoc Tests For One Way Anova
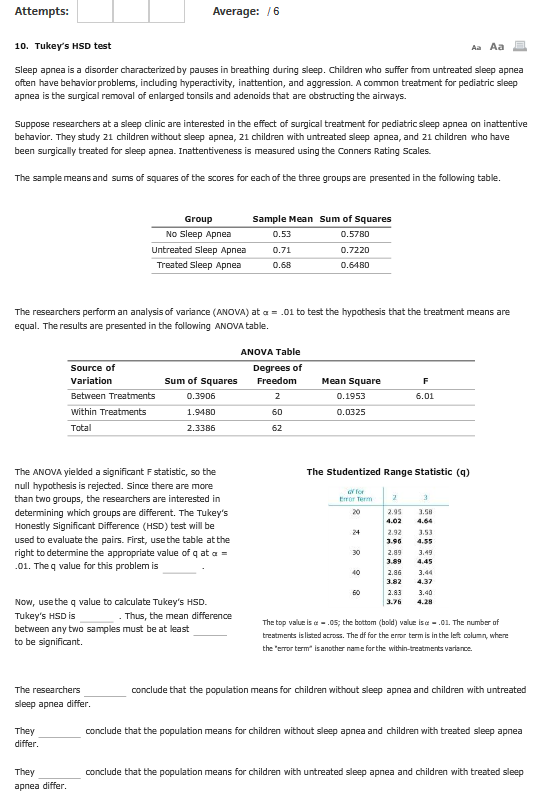



Stumped On This Stats Problem Tukey S Hsd Test Chegg Com



Www Ars Usda Gov Arsuserfiles Rapidcalculationofq Pdf



Methods Sagepub Com Base Download Referenceentry The Sage Encyclopedia Of Communication Research Methods I Xml




How To Obtain Tukey Table In R Cross Validated




Post Hoc Tukey Hsd Test For Hypothesis Where The One Factor Analysis Download Table



Multiple Comparisons




Q Table For Tukey Pdf Table B 5 The Q Statistic Tukey Hsd Test K Number Of Treatments Levels Withingroups Df Alp Ha Lev El 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Course Hero




Tukey Hsd Test What Is The Tukey Hsd Test




How Is The Standard Error Used In Calculating A Tukey Hsd Defined And Calculated Cross Validated




Tukey Q Table




Tukey S Hsd Table Of Q Statistics For Esn Model Download Table



3




Oneway Anova Introduction To Analysis Of Variance Anova




Tukey S Honestly Significant Difference Ppt Download



Post Hoc Tests For One Way Anova




Tukeytable Table Q Scores For Tukeys Method 0 05 K Df 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 24 30 40 60 1 2 18 0 6 08 4 50 3 93 3 64 Course Hero




T U K E Y Q T A B L E Zonealarm Results



43 Q Distribution Table For Tukey Test


コメント
コメントを投稿